Intervals must have one of three types selected based on the nature of the maintenance strategy: meter-based, measurement-based, or time-based.
Meter-based |
Measurement-based |
Time-based |
|---|---|---|
•Generates orders based on a threshold stored in the Interval and the trend set by recorded meter values. •For example, if you require an elevator to be inspected every 1000 lifts and record meter readings at an average of 250/day, the system will generate inspection appointments every four days. •When selected from the Type drop-down menu on the Interval form, generates the Counter drop-down menu. •To fill out the Counter field, you must have added Operating Counter to the device's or component's version. |
•Generates orders based dates based on recorded values that fall outside of a range of pre-defined values. This is similar to meter-based intervals but instead of using a single threshold that readings must stay over or under, a measurement-based interval requires meter reading values to fall within a range of values defined in a threshold table. •For example, if you require the temperature in a sauna to remain within a range of degrees for the sauna to remain operational, the system will generate inspections if and when the recorded readings fall outside of a range defined in a threshold table. •When selected from the Type drop-down menu on the Interval form, generates the Measure, Limiting Size Type, and Counter drop-down menus. |
•Schedules orders to occur on a time-based schedule. You define the amount of time that should elapse between action dates. •When selected from the Type drop-down menu on the Interval form, generates the Interval field, in which the user can specify the daily, weekly, or monthly cadence of the action dates, and a Basis for previous target date (otherwise execution) check box. •If the user selects the Months option from the Interval drop-down menu, the form generates a Last day of the month check box, which allows the user to specify that an action date should always fall on the last day of the month. |
Examples
Examples of the three types of intervals are outlined below.
Meter-based
In this example, we'll show how a maintenance strategy with a meter-based interval can be used to generate action dates using meter readings that record how many trips an elevator takes. The system will generate orders based on when it determines that the lift counter will surpass the threshold that was specified.
To add a meter-based Interval to a maintenance strategy, you must have already created an operating counter that measures the units read by the meter and applied it to the version associated with the maintenance strategy. In this example, we've created a meter called Elevator Lift Counter that counts the number of lifts an elevator makes.
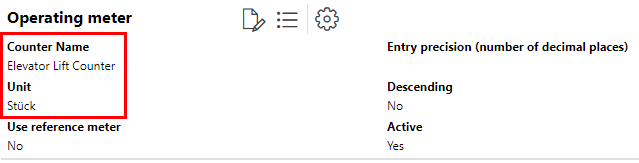
The meter is then applied to the version for the elevators whose lifts we want it to count. In this example, we have applied to the version for passenger elevators.
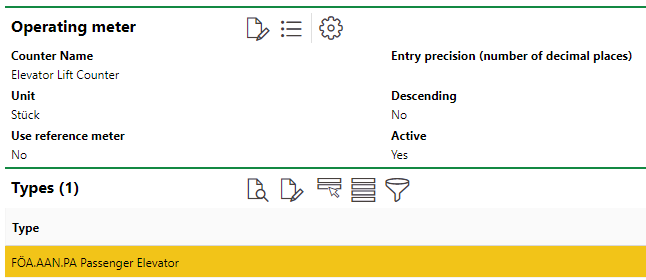
Then, we create a new maintenance strategy for the passenger elevator version. After we have added the maintenance strategy to the version, we add an interval to the maintenance strategy. Because we are creating a meter-based Interval in this example, we want to select Meter-based from the Type drop-down menu. When you make this selection, the form generates the Counter and Interval fields.
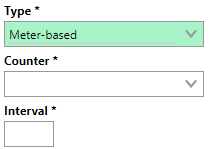
From the Counter drop-down menu, you can now select any operating meters that have been added to the system and applied to the version. When you select an operating meter, the unit that the meter measures displays next to the Interval box.
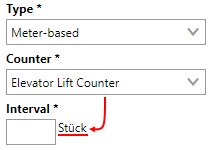
We can now enter a value that, along with the unit associated with the counter, will serve as the threshold. In this example, we'll say that the elevator should be exceeded based on a the meter's exceeding 1000 lifts.
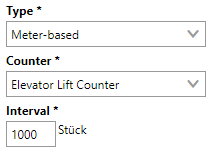
When the rest of the form is completed, we can save the interval.
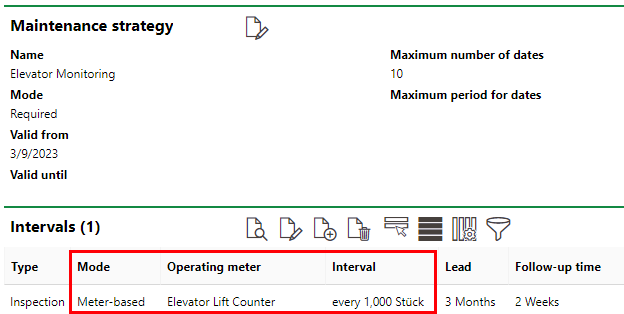
New Interval Added to the Maintenance Strategy Details Page
We can now being recording readings on the meter. From the Add Operating Meter workflow, double-click the meter that is associated with the maintenance strategy interval.
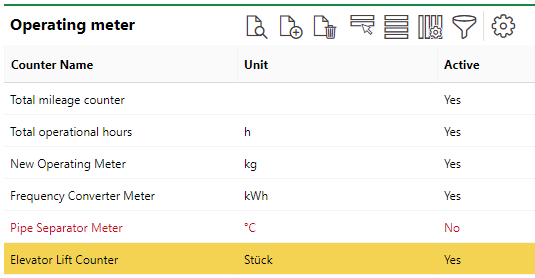
Operating Meters Table
We can then add a meter reading for any of the devices. We will need to enter at least two meter readings for the system to generate future appointments based on the trend of the meter readings over time. For this example, we will say the number of lifts counted for Passenger Elevator #1 on March 9, 2023, was 250.
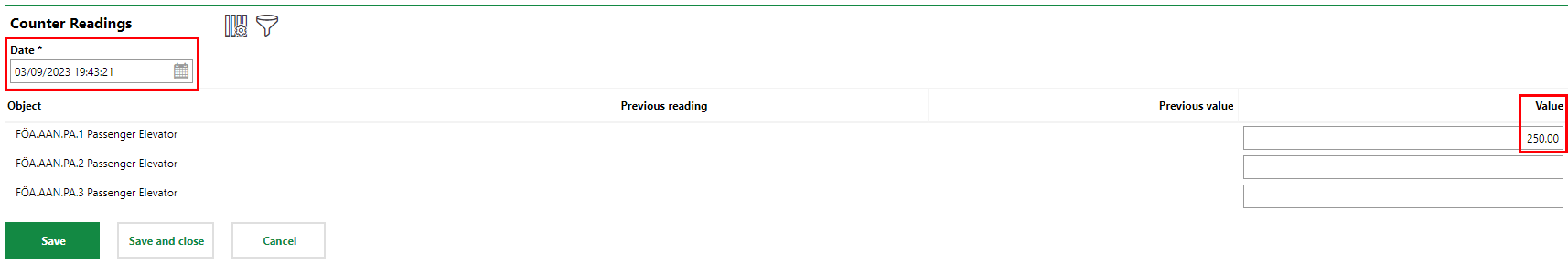
First Reading
On March 10, the meter for this elevator indicated 500. This recording can be entered in VertiGIS FM Maintenance as the new value.
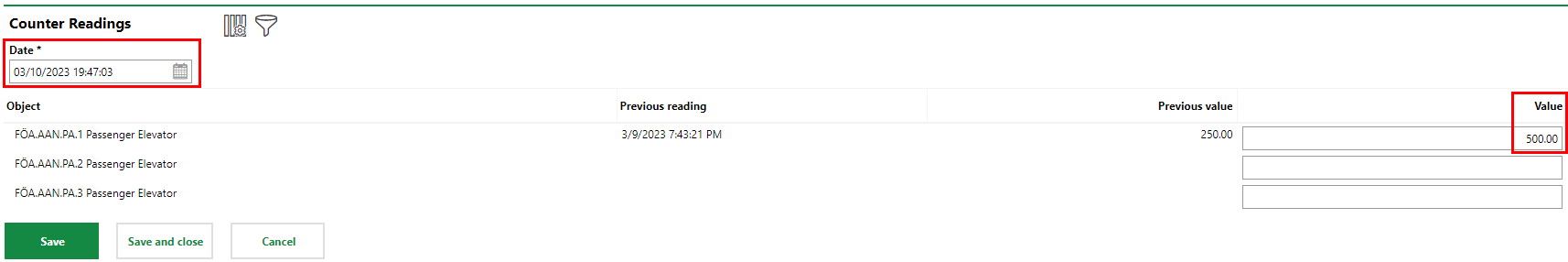
Second Reading
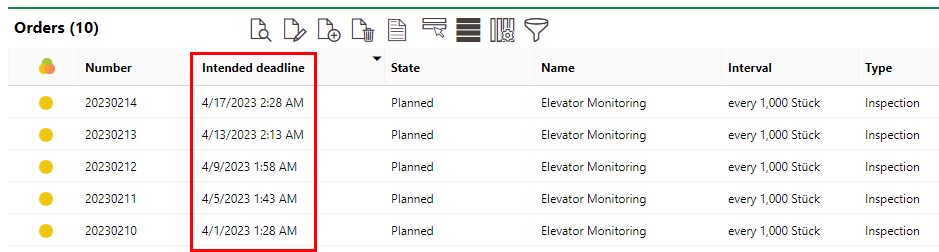
Because the meter indicated 250 on the first day and 500 on the second day, we have established a current trend of 250 lifts per day on Passenger Elevator #1. If you navigate to the device page for this elevator, you can see this trend reflected in the cadence of inspection appointments for the elevator that have been generated. Because the Interval threshold is 1000 and we have recorded meter readings of 250 lifts per day, the system has scheduled inspections every 4 days (1000/250 = 4). It has used the Maximum number of dates value we entered (10) and scheduled 10 appointments into the future every 4 days.
Measurement-based
In this example, we will show how a maintenance strategy with a measurement-based interval can be used to generate action dates using meter readings for a sauna whose temperature must fall within a certain range for it to be operational. The system will generate actions dates based when meter readings indicate that the temperatures are or are trending outside of the specified range.
To establish a measurement-based interval, we will also need to create a measure and a threshold table at the sauna's group level in the Building Service Structure.
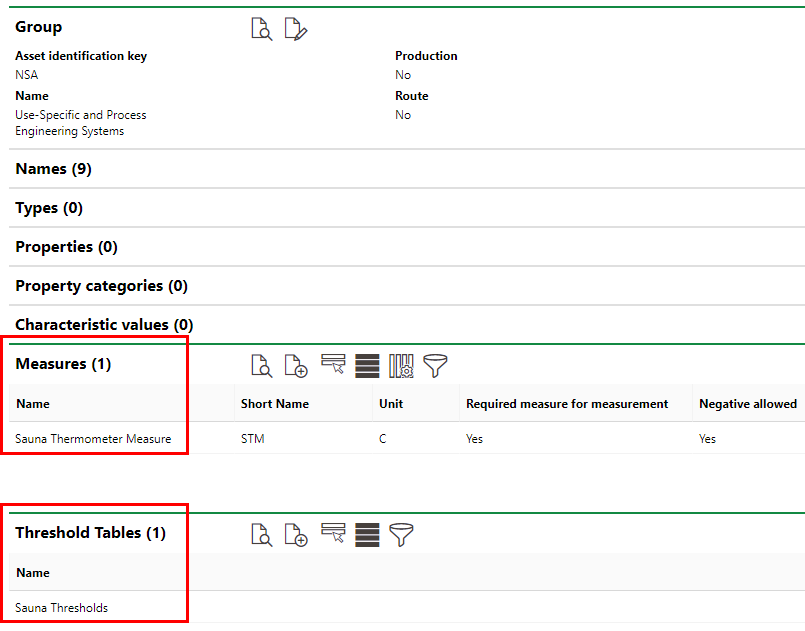
After creating the threshold table at the sauna's group level, we will apply it to the sauna's version.
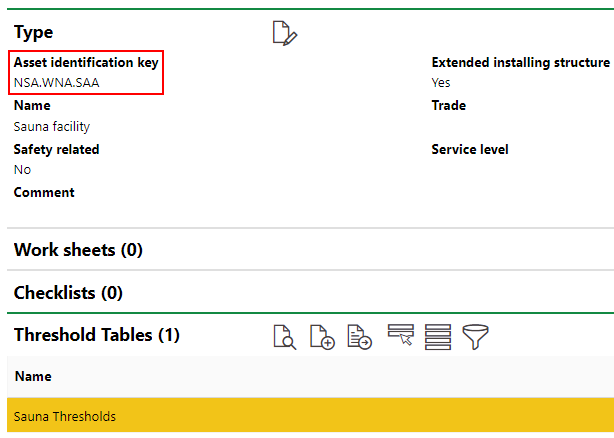
With a measure and threshold table established for the sauna's group, we can now create a new maintenance strategy for the sauna version. After we have added the maintenance strategy to the version, we add an interval to the maintenance strategy. Because we are creating a measurement-based Interval in this example, we want to select Measurement-based from the Type drop-down menu. When you make this selection, the form generates the Measure, Limiting Size Type, and Counter drop-down menus.
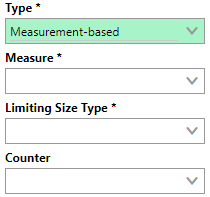
From the Measure drop-down menu, select the Celsius measure you created for the sauna.

From the Limiting Size Type drop-down menu, select the range within the threshold table you want to use to generate future action dates. In this example, we'll use the inspection limit (72-88 C°).
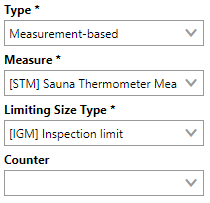
When the rest of the form is completed, we can save the interval.
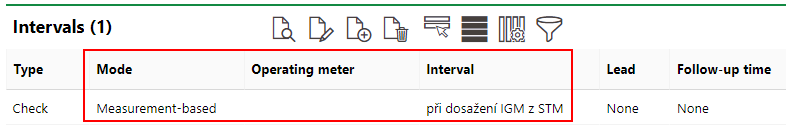
We can now register measurement data for the sauna in the Data section on the device details page. Note that the Data section does not display on the device details page unless the threshold table has been applied to the version.
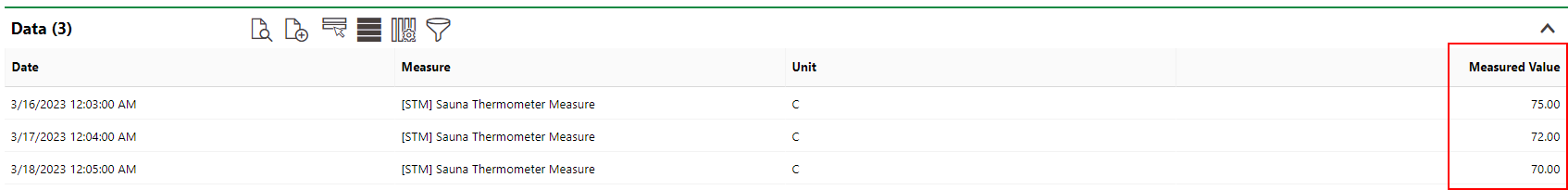
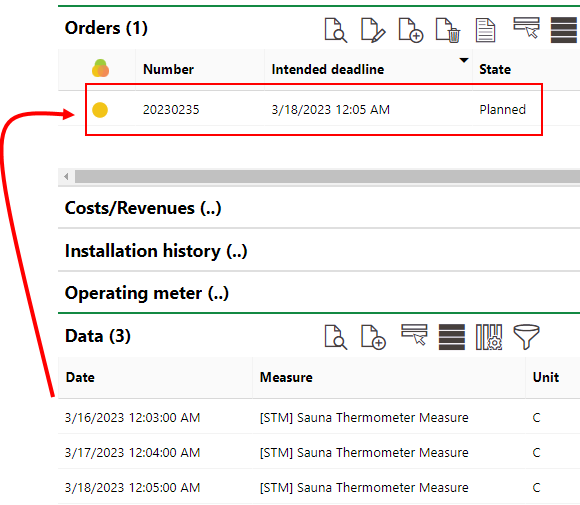
As the measured values have dropped below the inspection limit specified in the threshold table, the system has generated an appointment to inspect the sauna.
Time-based
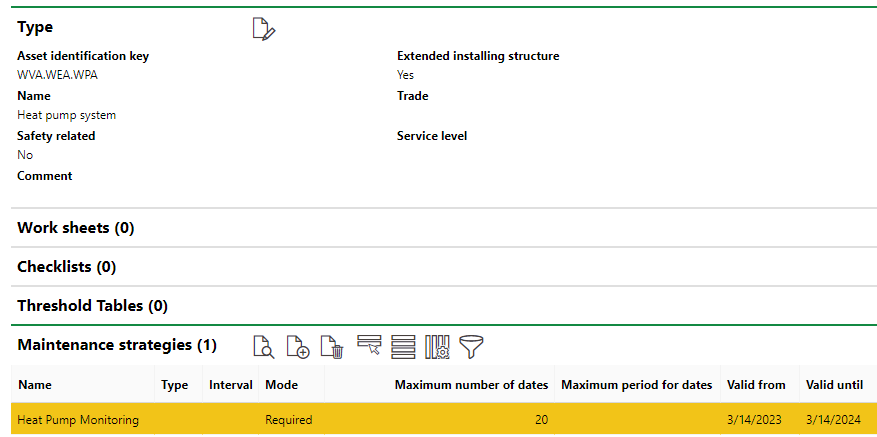
In this example, we will show how a maintenance strategy with a time-based interval can be used to generate action dates for a heat pump based on a specified amount of time elapsing.
Because no meters or measurements are required for this maintenance strategy, we can immediately create the new maintenance strategy at the version level for the execution.
Now, we will add an interval to the maintenance strategy by double-clicking on the Heat Pump Monitoring strategy and clicking the Add (![]() ) icon in the Intervals section on the maintenance strategy details page.
) icon in the Intervals section on the maintenance strategy details page.
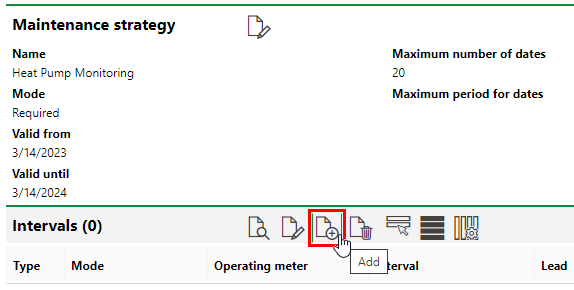
In the interval form, select Time-based from the second Type drop-down menu. This selection generates an Interval text box with a conjoined drop-down menu.
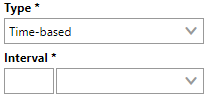
In the Interval fields, you specify how frequently you want the maintenance strategy to occur. For the purpose of this exercise, we will say the the heat pump required a routine inspection every two days, so we will type 2 in the text box and select Days from the drop-down menu.
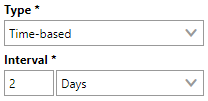
When the rest of the form has been filled out, you can click Save and Close to add the interval to the maintenance strategy. Click here for information about how to complete the rest of the fields on the interval form.
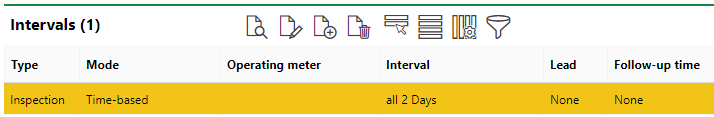
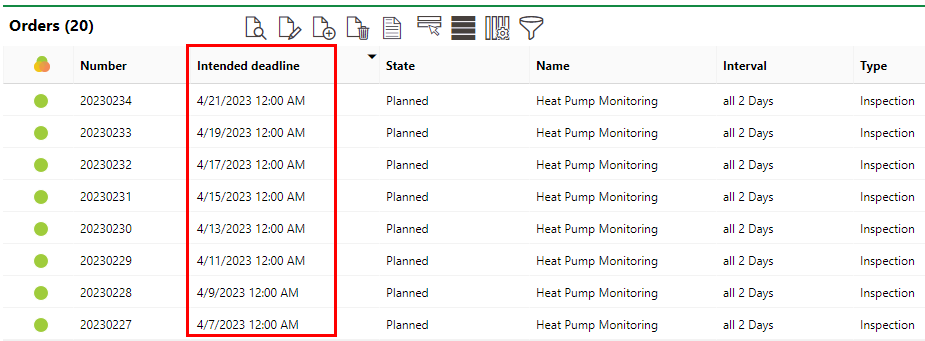
The system has now scheduled heat pump inspections every two days. To view the appointments, expand the Objects section on the maintenance strategy details page and double-click the individual heat pump.
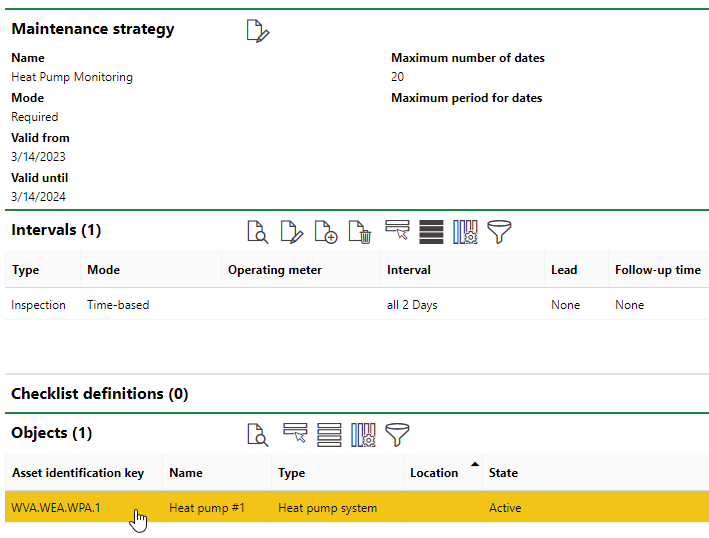
In the Orders section on the object details page for Heat Pump #1, you will see that the system has scheduled inspections every two days, as specified in the maintenance strategy interval.