Term |
Definition |
|---|---|
API (Application Programming Interface) |
An interface to an application which allows other applications to communicate with it. |
ArcGIS Server |
Software that makes it possible to create GIS services over the web for web mapping applications. |
Standard endpoints are hosted in a global cloud infrastructure, including the United States. The services are high-performance and optimized to use cloud resources closest to your geographic region. Check out the ArcGIS documentation for more details. |
|
A feature layer is a grouping of similar geographic features, for example, buildings, parcels, cities, roads, and earthquake epicenters. Features can be points, lines, or polygons (areas). Feature layers are most appropriate for visualizing data on top of your basemaps. |
|
Firewall |
A network security system that controls incoming and outgoing network traffic. |
Framework |
Software that provides generic functionality, which you can customize for different applications. For example, the HTML5 Viewer framework enables you to add HTML5 viewers that are customizable. |
GIS (Geographic Information System) |
A system that captures, analyzes, or manages data that is linked to a location on a map. |
A human-readable name that stands for an IP address. For example, www.mydomain.com and support.mydomain.com are host names. |
|
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) |
The Internet protocol used to deliver information over the World Wide Web. |
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) |
A message transfer protocol used by the World Wide Web to service page requests, and which adds a security layer using Secure Socket Layer (SSL) technology. |
IP Address (Internet Protocol address) |
A numeric label that uniquely identifies a computer or other device connected to a network that uses Internet Protocol. For example, 192.168.1.1 is an IP address. See also: Host Name. |
In a coverage, a feature class used to represent points or identify polygons. When representing points, the x,y location of the point describes the location of the feature. When identifying polygons, the point can be located anywhere within the polygon. |
|
Layer |
The data in web maps is usually represented in layers, for example, roads would be on a separate layer from rivers and waterways and political boundaries would be on a separate layer from national parks. A Group Layer is a group of several layers that look and behave like a single layer. |
Map |
Web-based maps are fundamentally different from paper-based maps in that they are both interactive and searchable. Web-based maps contain data in many forms, which can be searched and annotated. |
REST (Representational State Transfer) |
An architectural style used for network applications. Communication between the Studio Search, Portal, viewers, and ArcGIS Server is done using REST. |
A web-based, REST-compatible representation of the configuration of one or more web mapping applications. The REST API is organized as a hierarchy (a tree). Studio Search can obtain configuration information by making HTTP requests to the REST API. Check out REST API for more information. |
|
REST Endpoint |
The items in a REST API's hierarchy are called "endpoints". Each endpoint represents the configuration of a particular resource or operation in the site. Each endpoint has a unique URL, which enables viewers to identify individual endpoints. |
SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) |
A network protocol to exchange messages in XML format between systems. The messages are transported via HTTP or HTTPS. |
SSL (Secure Socket Layer) |
The protocol that improves the security of data communication by using a combination of data encryption, digital certificates, and public key cryptography. SSL enables authentication and increases data integrity and privacy over networks. SSL does not provide authorization or nonrepudiation. |
Service |
In the context of web mapping, services are GIS resources that are located on a server and accessed over a network. Types of service include map services, feature services, and geocoding services. |
Site |
A technology-neutral configuration of a GIS application. A site's configuration is stored in XML format. Each site has its own configuration file called Site.xml. |
Tree |
A hierarchy, called a "tree" because it looks like an upside-down tree when represented graphically. The items in a tree are called "nodes". In a REST API, the nodes are called "endpoints". See also: REST Endpoint. 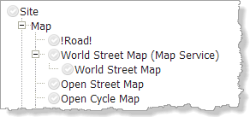 |
URI (Uniform Resource Identifier) |
A string that identifies a resource on a computer or computer network. URIs enable interactions over the Internet using protocols. |
URL (Uniform Resource Locator) |
A type of URI. Commonly known as a web address. |
Viewer |
Viewers are the web applications that end users run to interact with a site and its map. |