In simple terms, active equipment in a telecommunications network refers to powered devices that process or boost signals. These are the components that need electricity to operate and play an active role in managing, amplifying, switching, or routing data.
|
|
|

|
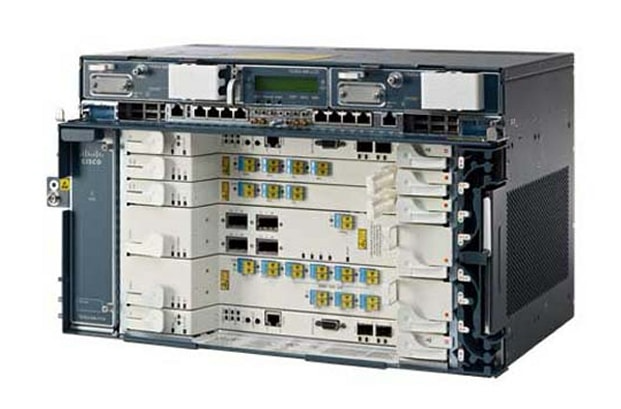
A multiplexer (often abbreviated as MUX) is a device that combines multiple signals into one single signal. It's like a traffic manager for data, allowing several signals to share the same channel or TEL line. Multiplexers are considered active equipment and typically have many slots with many different card options.
|
|
|
|
|

|
DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) equipment is used in optical networking to increase bandwidth over existing fiber infrastructure by multiplexing multiple wavelengths (channels) of light onto a single fiber. DWDM equipment are considered active and typically have many slots with many different card options. Several different types of shelves may be combined to form a single DWDM device.
|
|
|
|
|

|
An OLT (Optical Line Terminal) is a key device in a PON (Passive Optical Network) architecture, typically located at a central office. It manages traffic between the core network and multiple ONUs/ONTs (Optical Network Units/Terminals) at customer premises. OLTs are considered active equipment and typically have many slots with many different card options.
|
|